1. Subcellular Localization Service Overview
Subcellular localization is an essential experimental approach to study the spatial distribution of target genes or proteins within plant and animal cells. This technique helps researchers understand protein function and reveals their roles in signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms.
YBioHub provides a professional localization platform using both plant and animal cell systems, ensuring fast and accurate results.
2. Principle of Subcellular Localization
Subcellular localization is commonly achieved through fluorescent tagging:
- Fusion of the target gene with fluorescent proteins (e.g., GFP, RFP, YFP).
- Introduction of the fusion construct into cells (systems include tobacco leaves for transient expression, Arabidopsis stable transformation, yeast, or mammalian cells).
- Observation of fluorescence signals under a confocal or fluorescence microscope.
- Comparison of signals with organelle-specific markers (nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, ER, etc.) to determine localization.
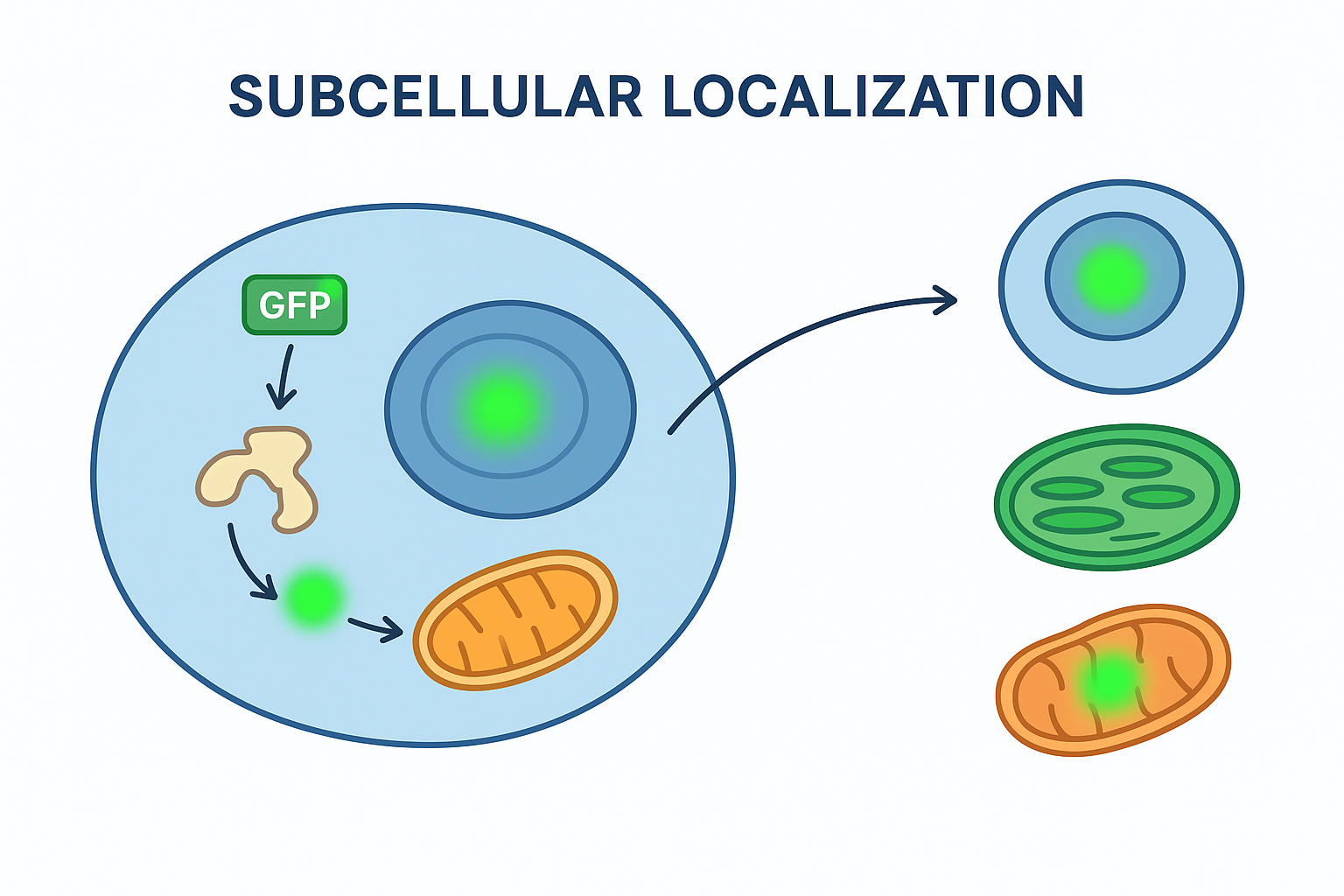
Figure: Visualization of GFP-tagged proteins in plant and animal cells.
3. Experimental Workflow (Simplified)
- Gene cloning & vector construction
- Transformation/transfection
- Fluorescence microscopy
- Data analysis
4. Applications of Subcellular Localization
- Characterization of novel gene functions
- Verification of protein roles in signaling pathways
- Insights into organelle-associated molecular mechanisms
- Support for genetic engineering and crop improvement
5. Service Advantages (YBioHub)
- 📌 Experienced team, skilled in multiple localization systems
- 📌 Support for various fluorescent tags (GFP, RFP, YFP, etc.)
- 📌 High-quality microscopy imaging and analysis
- 📌 Fast turnaround, clear and reliable results
6. Deliverables
- Fluorescence microscopy images
- Experimental analysis report
- Raw data files (upon request)
7. FAQ
Q1: Which systems are commonly used for subcellular localization?
A: Plant transient expression (tobacco leaves), Arabidopsis stable transformation, yeast, and mammalian cells are frequently applied.
Q2: How long does the experiment take?
A: Typically 2–4 weeks, depending on the host system and project design.
Q3: Can specific organelle markers be included?
A: Yes. Clients can specify markers, and we also provide commonly used organelle markers.
Q4: I only have the gene sequence, not the vector. Can I still order this service?
A: Yes. We provide one-stop service from gene cloning to vector construction.
Q5: What will I receive as the final results?
A: You will receive fluorescence images, a localization analysis report, and raw data if required.